Drilling Rig Components
Rotary System:
The rotary system plays a crucial role in rotating the drill string and, in turn, the drill bit at the bottom of the borehole.* Rotary Table: This is a traditional method, which is still commonly used, especially on land rigs. It involves several components, as follows. This turntable creates rotational motion, transferring it to the drill pipe and bit via the equipment. It is powered by either an electric motor or a system of gears and chains connected to the rig drawworks. Additionally, various components ensure that the rotational movement of the turntable is smoothly transmitted to the drill pipe and the attached bit.
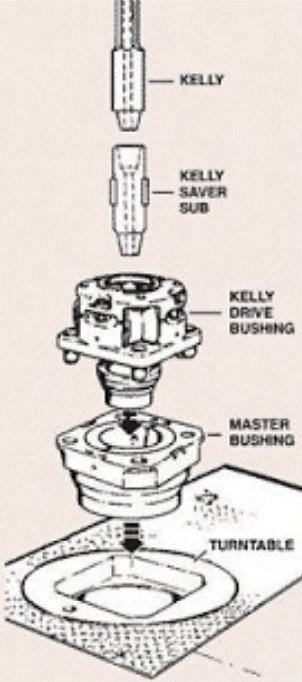
* Master bushing: The ‘Master bushing’ fits tightly within the turntable. As the turntable rotates, it rotates the master bushing. The master bushing has an opening, which enables crew members to run the pipe directly into the wellbore.
* Kelly drive bushing: The Kelly drive bushing is installed when drilling with a Kelly. The master bushing transfers torque and rotation from the rotary table to the Kelly bushing. The external profile of a Kelly snuggly fits inside the Kelly bushing. Hence, the torque is effectively transmitted to the Kelly, which is connected to the drill string while drilling.
* Kelly saver sub: A Kelly is connected to the drill stem. The connection wear occurs each time the Kelly is made up to the drill stem components. Hence, the Kelly saver sub is used between Kelly and the drill stem, taking all the connection wears. The saver sub connection is sacrificed because it can be easily repaired or replaced, thus prolonging the life of the Kelly.
* Kelly: Kelly is a heavy square or hexagonal steel member suspended from the swivel through the rotary table and connected to the topmost joint of the drill pipe. It transmits the rotation from the Kelly bushing to the turn of the drill stem and the bit as the rotary table turns.
Top Drive: A modern alternative to the conventional rotary system. The top drive rotates the drill string and bit without using a kelly and rotary table, increasing efficiency and safety. The top drive is operated from a control panel on the rig floor.
Drawworks: The Drawworks is an assembly of a rotating drum, a series of shafts, clutches, chains, and gears for changing speed and reversing. It’s a large winch system that reels out and reels in the drilling line to raise or lower the drill string and manage the weight of the drilling assembly.
Derrick/Mast: The derrick or mast is a tall, vertical structure on a drilling rig that supports the lifting and lowering of the drill string during drilling operations. It serves as the primary framework for hoisting equipment, such as the traveling block and drill pipe, allowing for efficient handling of heavy loads.
* Derrick: Typically, a stationary, four-legged structure that provides exceptional stability for long-term operations.
* Mast: A mobile, collapsible alternative often used on rigs that must be transported and reassembled quickly.
Both structures are crucial for enabling the vertical movement of equipment and ensuring the rig's operational efficiency.
Crown Block: A part of the drilling rig's hoisting system, the crown block is mounted at the top of the derrick or mast and consists of a set of pulleys or sheaves that guide the drill line, supporting the weight of the traveling block and drill string.
Travelling Block: A component of the hoisting system that moves up and down the derrick or mast, supporting the drill string and allowing for the raising and lowering of the drill pipe during operations.
Drill Line: A strong steel cable or rope used in the drilling rig that is reeved on sheaves of the crown block and traveling block to raise and lower the traveling block, drill string, and other equipment. It transmits the weight and force needed for drilling.
Kelly Hose: Also called Rotary Hose, this flexible hose connects the rig's mud system and standpipe to the drill pipe. It allows the flow of drilling fluid from the rig to the wellbore during drilling and circulation.
Gooseneck: A section of pipe with a bent shape used to direct drilling fluids into the drill string, often part of the system connecting the rig’s pumps to the well.
Standpipe: A vertical pipe used to transport drilling fluid from the mud pumps to the rig floor or to the Kelly hose, providing the necessary pressure for circulating fluids during drilling.
Hoses: Flexible tubes used throughout the rig to carry drilling fluids, power, or other materials, connecting various parts of the drilling system, including the mud pumps, standpipes, and choke lines.
Racking Board (Monkey Board): A raised platform on the rig where drill pipes are stored between trips in and out of the well, allowing for efficient management of pipe connections during drilling operations.
Rig Floor: The flat surface area on the drilling rig where operations such as pipe handling, drilling, and equipment management take place, typically located directly beneath the derrick.
Doghouse: A small enclosure on the rig floor used as an office for the driller and shelter on the rig floor for the crew members at work. It is often equipped with basic amenities for workers and stores small objects required for operations from time to time.
Bell Nipple: A short pipe section connecting the Kelly hose to the top drive or rotary system, ensuring a secure and leak-free connection during drilling.
Blowout Preventer (BOP): A critical piece of safety equipment installed at the wellhead, designed to prevent uncontrolled pressure from escaping the well during drilling operations. It contains valves that seal the annular space between the pipe and well bore in a well control situation or blow-out.
Wellhead: The equipment installed at the surface of the wellbore to provide access to the well and control pressure, including the casing head and tubing head. A BOP stack is installed on the wellhead during drilling, completion, and workover operations. A Christmas tree is installed once the well is complete and needs to be hooked up for production.
Christmas Tree: An arrangement of valves, spools, and fittings installed on the wellhead to control the production of oil and gas, including safety and monitoring devices to manage well flow. It is used on self-flowing wells where reservoir pressure is sufficient for the reservoir fluid to flow to the surface.
Choke and Kill Manifolds: These are an arrangement of piping and special valves, called chokes, through which drilling mud is circulated when the blowout preventers are closed to control the pressures encountered during a kick. The choke manifold controls the flow of fluids from the well to the surface, while the kill manifold pumps heavy fluids into the wellbore as required to control a well.
Safety Valves: Safety Valves are designed to automatically close in the event of a malfunction or emergency, helping to contain pressure and prevent spills or accidents.
Flow Line: These pipes transport the drilling or production fluids from the wellhead to other processing or storage areas, playing a key role in fluid circulation during drilling and production.
Power Generation System: The equipment used to generate the electrical power required to operate various systems on the rig, including mud pumps, hoisting systems, and lighting.
SCR (Silicon Controlled Rectifier): A type of power converter used to control the electrical current for the rig’s power system, ensuring that electrical power is distributed efficiently to the rig's equipment.
Elevators and Slips:
* Elevators: Tools used to lift and position heavy equipment, like drill pipe or casing, during rig operations.
* Slips: Devices used to secure the drill string or casing when making or breaking connections. It prevents the string from falling into the wellbore.
Mud pumps circulate drilling fluids (mud) downhole to cool and lubricate the bit, carry cuttings to the surface, and maintain the required pressure within the wellbore for efficient drilling and completion operations.
Mud Tanks: Large containers used to store and circulate drilling fluids, typically part of the solid control system, where the mud is mixed, processed, and stored before being pumped into the well.
Hopper (Mud Additive Mixer): A device used to mix and prepare drilling fluid additives (such as bentonite, barite, or polymers) into the base drilling fluid, helping to achieve the required properties for effective drilling.
